The Mystery of Sleep: Why We Sleep and Its Health Effects
Sleep remains one of the most mysterious and essential aspects of human existence. Despite significant advances in medical and psychological research, there is still much we do not fully understand about why we sleep. What is clear, however, is that sleep is integral to overall health and well-being. In this post, we explore why we sleep and the profound effects it has on our health.
Understanding Sleep: The Basics
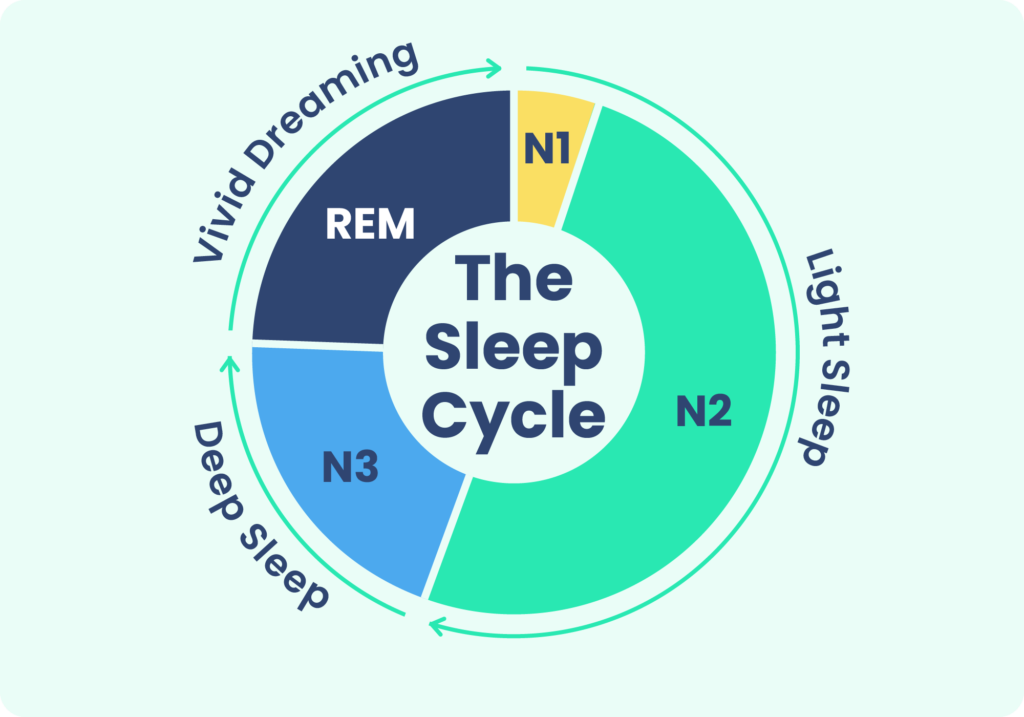
Sleep is a complex process that involves various stages, each serving different functions necessary for health. The two primary types of sleep are rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. Together, they cycle through approximately every 90 minutes.
Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) Sleep
NREM sleep is divided into three stages:
- Stage 1: This is the lightest stage of sleep, where you transition between wakefulness and sleep. Your heartbeat and breathing slow down, and your muscles relax.
- Stage 2: In this stage, your body temperature drops, and sleep spindles (sudden bursts of brain activity) occur. This stage accounts for about 50% of your total sleep time.
- Stage 3: Known as deep sleep or slow-wave sleep, this stage is crucial for physical restoration. During this period, the body repairs tissues, builds muscle, and strengthens the immune system.
Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Sleep
REM sleep is characterized by rapid movement of the eyes, increased brain activity, and vivid dreams. This stage is essential for cognitive functions such as memory consolidation, learning, and emotional regulation.
Why Do We Sleep?
The exact reasons why we sleep are still debated, but several theories have emerged over the years:
Restorative Theory
This theory suggests that sleep serves to restore, repair, and rejuvenate the body. Research has shown that specific physiological processes occur predominantly during sleep, such as muscle growth, tissue repair, protein synthesis, and the release of vital hormones.
Energy Conservation Theory
According to this theory, the primary function of sleep is to reduce energy demand and expenditure during part of the day or night. By sleeping, humans reduce their metabolic rate and subsequently conserve energy.
Brain Plasticity Theory
Sleep plays a crucial role in brain function and plasticity. During sleep, the brain processes the information acquired throughout the day, consolidates memories, and makes connections between new and existing memories. This process is indispensable for learning and cognitive performance.
Brain Detoxification Theory
A relatively recent theory suggests that sleep is crucial for clearing out neurotoxic waste products that accumulate in the brain during wakefulness. This cleaning process, conducted by the brain’s glymphatic system, is thought to help prevent neurodegenerative diseases.
The Health Effects of Sleep
Adequate sleep is vital for maintaining overall health. Chronic sleep deprivation can have serious consequences on physical, mental, and emotional well-being. Below are some key health effects of sleep:
Physical Health
Quality sleep contributes significantly to various aspects of physical health:
- Immune Function: Sleep is essential for a healthy immune system. During sleep, your body produces and releases cytokines, which help fight infections and inflammation.
- Cardiovascular Health: Poor sleep has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, hypertension, and stroke. Sleep helps regulate blood pressure, and chronic sleep deprivation can lead to long-term cardiovascular problems.
- Weight Management: Sleep influences hormones that control hunger and appetite, such as ghrelin and leptin. Lack of sleep can lead to weight gain and obesity.
- Diabetes Risk: Inadequate sleep impairs the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Mental Health
Good sleep is critical for mental and emotional well-being:
- Mood Regulation: Sleep affects the brain’s ability to regulate emotions and handle stress. Sleep deprivation can lead to irritability, mood swings, and increased anxiety.
- Cognitive Functions: Sleep is essential for concentration, problem-solving, and decision-making. Lack of sleep impairs cognitive functions, making it difficult to think clearly and make decisions.
- Mental Health Disorders: Chronic sleep issues are linked to mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. Quality sleep can provide a natural remedy for improving mood and mental health.
Learning and Memory
Sleep is crucial for learning and memory consolidation:
- Memory Consolidation: Research shows that sleep plays a vital role in consolidating memories. During sleep, the brain processes information and strengthens neural connections formed during wakefulness.
- Learning: Adequate sleep enhances your ability to learn new information and skills. During sleep, the brain organizes and integrates new information with existing knowledge, making it easier to recall and apply.
Improving Sleep Quality
To reap the health benefits of sleep, it is essential to prioritize and maintain good sleep hygiene. Here are some tips for improving sleep quality:
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down.
- Ensure your sleep environment is comfortable, dark, cool, and quiet.
- Avoid caffeine, nicotine, and heavy meals close to bedtime.
- Limit exposure to screens and blue light before going to bed.
- Engage in regular physical activity, but avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime.
By prioritizing sleep and making these changes, you can significantly improve your overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
Although sleep remains a complex and not entirely understood phenomenon, its importance for health is undeniable. From physical restoration to cognitive processing, sleep affects nearly every aspect of our lives. By understanding why we sleep and its health effects, we can take actionable steps to improve our sleep quality and, in turn, our overall well-being.
For more detailed insights on sleep and its benefits, you can refer to resources like the Sleep Foundation.


