Compilation in GoLang: Translating Code to Machine Language
Hey there, tech enthusiasts! If you’re fascinated by programming languages and how your code gets transformed into silky-smooth operations within your machine, then you’re in the right place. Today, we’re delving into the world of GoLang compilation — a captivating journey from human-readable code to machine-understandable instructions. Buckle up!
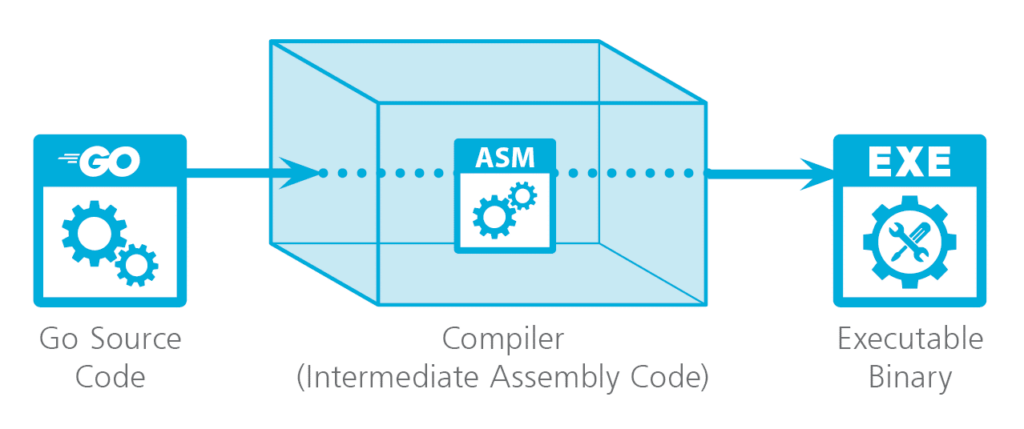
Understanding the Compilation Process
First things first, what exactly is compilation? In simple terms, compilation is the process of translating code written in a high-level programming language like Go into machine code that your computer’s CPU can execute. Think of it as converting a gourmet recipe (your GoLang code) into a series of precise cooking steps (binary instructions) that a robot chef (your CPU) can follow.
Why Compilation Matters
Before we dive deeper, let’s grasp why compilation is essential. The primary reasons are error detection, optimization, and performance. Compilers analyze your code to spot any errors early, optimize it to improve efficiency (eliminating redundant steps, for instance), and ultimately convert it to machine code for faster execution. With GoLang, the compiler does an incredible job ensuring your programs run swiftly and smoothly.
GoLang’s Compiler: An Overview
GoLang uses its own compiler called gc (Go Compiler). It’s designed to be fast, efficient, and straightforward, allowing Go developers to compile and execute their programs quickly. The gc compiler is part of the Go toolchain, which includes tools like go build, go run, and go install.
The Compilation Steps in GoLang
1. Lexical Analysis
The process begins with lexical analysis, where the source code is broken down into tokens. Tokens are the smallest units of meaning—keywords, identifiers, literals, and symbols.
2. Syntax Analysis
Next up is syntax analysis. In this phase, the compiler checks the tokenized code to ensure it follows the rules of the Go language grammar. If you’ve missed a semicolon or misplaced a bracket, this is where you’ll find out.
3. Semantic Analysis
During semantic analysis, the compiler ensures that your code makes sense logically. It checks for type mismatches, variable declarations, and scope issues, guaranteeing that the program is semantically valid.
4. Intermediate Code Generation
Once the semantics are verified, the compiler generates an intermediate representation (IR) of the code. This IR is a low-level, platform-independent code that provides a stepping stone between the source code and the final machine code.
5. Optimization
This is where the magic happens. The optimization phase improves the intermediate code’s efficiency without altering its functionality. It may inline functions, remove dead code, or simplify expressions to make the code run faster.
6. Code Generation
Finally, the intermediate code is translated into machine code specific to the target architecture (x86, ARM, etc.). The generated machine code is what your processor will execute directly.
The Role of the Go Command
The Go toolchain makes compilation easy with the powerful go command. Here are some common usages:
Build a Go Program
go build myprogram.goThis command compiles the source code and produces an executable binary. If myprogram.go has no syntax or semantic errors, you’ll get a shiny new binary to run.
Run a Go Program
go run myprogram.goIf you want to compile and run in one go (pun intended), use go run. This command compiles the Go source file and immediately runs the resulting binary.
Install a Go Program
go installThe go install command compiles the program and installs the resulting binary in your workspace’s bin directory.
Why GoLang? The Compilation Edge
GoLang stands out because of its efficient compilation process, which is faster than many other languages. The speedy compilation is a tremendous asset for developers who need to build and iterate quickly. Moreover, GoLang’s simplicity ensures that the compiled programs are reliable and easy to maintain.
Final Words and Further Reading
Our whirlwind tour of GoLang compilation ends here, but the adventure continues! If you want to delve deeper into the nuts and bolts of GoLang, check out this official Go documentation. It’s a treasure trove of detailed insights and best practices that’ll make you a GoLang maestro in no time.
In conclusion, the compilation process in GoLang is both an art and a science, meticulously transforming your high-level code into machine-level instructions. By understanding each step, you can write better, more efficient programs. So keep coding, stay curious, and remember — the world of technology is vast and ever-evolving, with countless wonders waiting to be discovered!
Stay enthusiastic, keep learning, and look forward to our next tech exploration. Until then, happy coding!


