Explore how to effectively integrate LLM-generated code in production environments, focusing on practical architecture and real-world performance.


Explore how to effectively integrate LLM-generated code in production environments, focusing on practical architecture and real-world performance.

Discover how meticulously defined acceptance criteria maximize LLM performance in production environments, ensuring accuracy and operational efficiency.

Explore OpenAI’s GPT-5.3 Instant update, its enhancements, benchmarks, and implications for AI deployment in production environments.

Explore CMU’s 10-202 course on modern AI, focusing on LLM mechanics like ChatGPT, with hands-on assignments and practical skills.

Discover Mercury 2, the fastest reasoning LLM powered by diffusion, revolutionizing production AI with unprecedented speed and efficiency.

Explore how Hugging Face Agent Skills enhance LLM agents’ performance based on SkillsBench insights and practical applications.
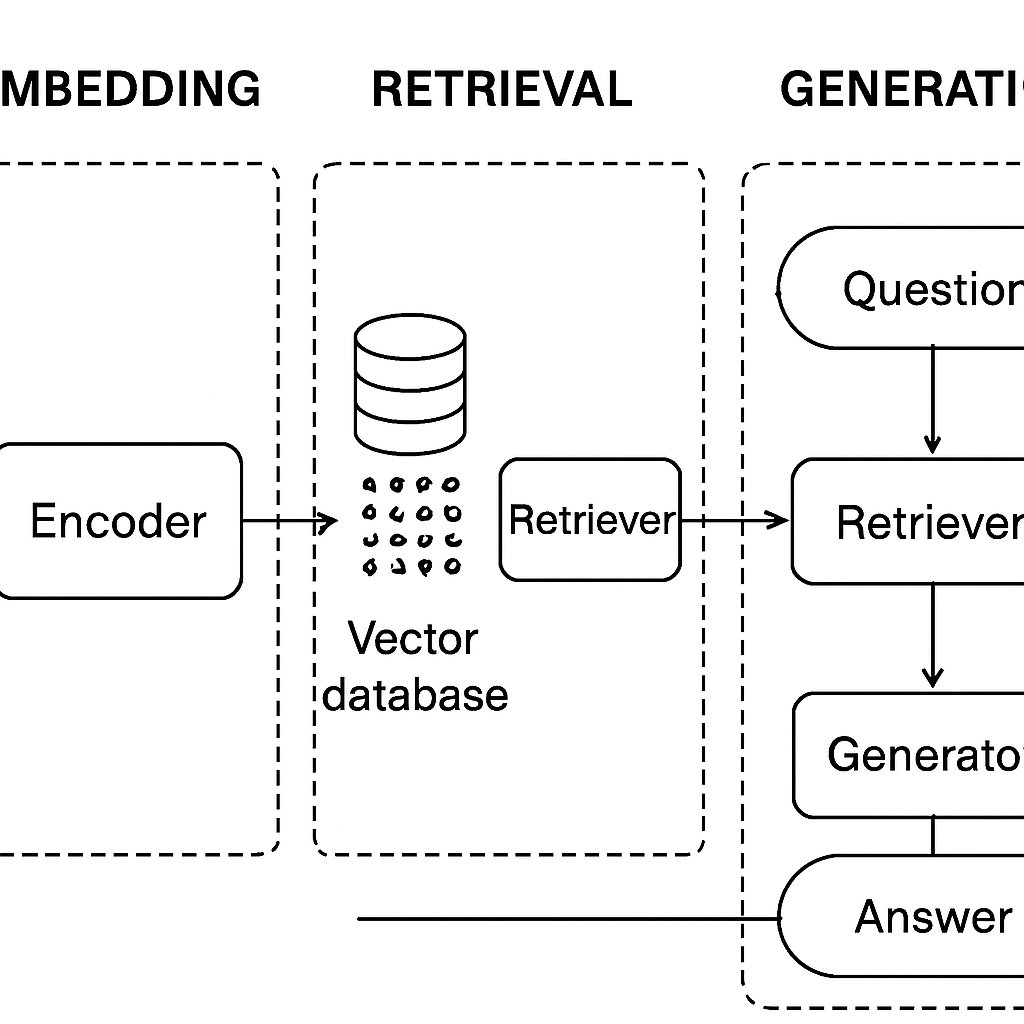
Learn to implement a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline for enterprise knowledge using code examples and cost analysis.